1
/
of
2
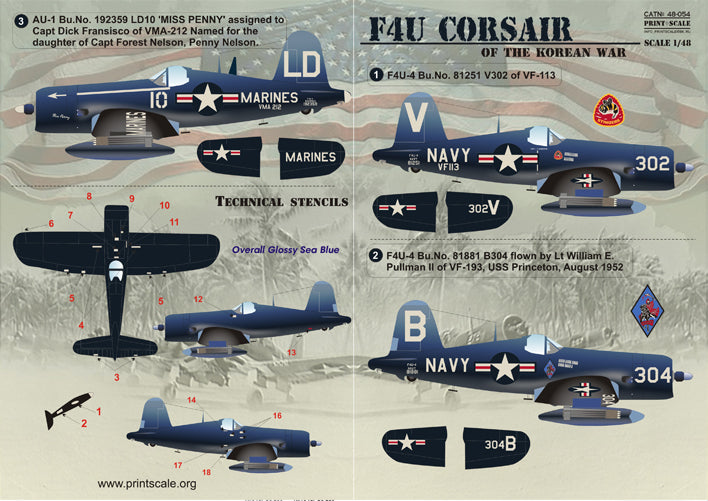
F4 U Corsair 1940 Year 1/48 Scale Decal Print Scale 48-054
F4 U Corsair 1940 Year 1/48 Scale Decal Print Scale 48-054
Regular price
$12.99 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$12.99 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Chance Vought F4U Corsair (eng. Chance Vought F4U Corsair) is a single-seat carrier-based fighter of the Second World War. Designed and built by Chance Vought, as well as Goodyear Aircraft (deck modification of the FG-1 for the fleet).
In 1938, the US Navy announced a competition for a new generation carrier-based fighter, in which Chance-Vote won. An agreement was signed with the firm for the construction of a prototype of a new aircraft in June 1938.
Most of the technical solutions in the design of the "Corsair" are dictated by the requirements of the military for the speed characteristics of the aircraft. To provide him with a high horizontal flight speed, the car was equipped with a 2000-horsepower air-cooled radial engine and an oversized four-blade propeller.
This gave rise to a number of difficulties that led to rather non-standard solutions. To provide the aircraft with the necessary safety during landing, the Corsair was equipped with a reverse gull wing, which made it possible to reduce the length of the landing gear without sacrificing the distance from the propeller to the deck. Also, a larger diameter propeller created a significant reactive moment. To compensate for it, the designers had to turn the keel of the aircraft 2 degrees to the left of the central axis of the fuselage.
A heavily curved "reverse gull" folding wing was designed, the main retractable landing gear legs were located at the wing break. May 29, 1940 pilot Lyman Billiard made a test flight. For the first time in the US aircraft industry, spot electric welding was used on the Corsair. On June 3, 1941, the Navy signed a contract with the company for the supply of 580 aircraft of this type.
In 1938, the US Navy announced a competition for a new generation carrier-based fighter, in which Chance-Vote won. An agreement was signed with the firm for the construction of a prototype of a new aircraft in June 1938.
Most of the technical solutions in the design of the "Corsair" are dictated by the requirements of the military for the speed characteristics of the aircraft. To provide him with a high horizontal flight speed, the car was equipped with a 2000-horsepower air-cooled radial engine and an oversized four-blade propeller.
This gave rise to a number of difficulties that led to rather non-standard solutions. To provide the aircraft with the necessary safety during landing, the Corsair was equipped with a reverse gull wing, which made it possible to reduce the length of the landing gear without sacrificing the distance from the propeller to the deck. Also, a larger diameter propeller created a significant reactive moment. To compensate for it, the designers had to turn the keel of the aircraft 2 degrees to the left of the central axis of the fuselage.
A heavily curved "reverse gull" folding wing was designed, the main retractable landing gear legs were located at the wing break. May 29, 1940 pilot Lyman Billiard made a test flight. For the first time in the US aircraft industry, spot electric welding was used on the Corsair. On June 3, 1941, the Navy signed a contract with the company for the supply of 580 aircraft of this type.
Product features
Product features
Materials and care
Materials and care
Merchandising tips
Merchandising tips
Share